Answer
Puzzler 1: Peer to Peer Bandwidth
The differences in the duration of the P2P copies is due to the fact that the GPUs are connected to each other using different interconnects.
The network topology within a server can be obtained by executing nvidia-smi topo -m on the command
line. The most common interconnects are NVLink (a direct GPU-to-GPU interconnect within the server)
and PCIe. On our server, GPU0 and GPU1 are connected via 4 NVLinks, GPU0 and GPU4 are connected via
2 NVLinks and GPU0 and GPU2 are connected via PCIe.
With a 400 MB tensor the observed bandwidth is 93 GB/sec with 4 NVLinks, 47 GB/sec with 2 NVLinks and 7.5 GB/sec when using PCIe.
Puzzler 2: Collective Performance
While the All_Reduce, Reduce + Broadcast and Reduce_Scatter + All_Gather are mathematically equivalent their performance depends on:
- NCCL algorithm and protocol (NCCL algorithm is Nvidia speak for routing configuration)
- Network topology
- Number of GPUs
- Message size
Empirically, we tested the Ring and Tree Algorithms on 16 GPUs with 1GB and 2GB tensors (on each GPU) and observed the following timings (in milliseconds):
| 1GB tensor using Tree | 1GB tensor using Ring | 2GB tensor using Tree | 2GB tensor using Ring | |
| All Reduce | 2.2 | 4.7 | 4.6 | 13.5 |
| Reduce, Broadcast (Total) | 2.7, 0.8 (3.5) | 2.4, 3.0 (5.4) | 5.0, 1.7 (6.7) | 7.4, 3.8 (11.2) |
| Reduce Scatter, All Gather (Total) | 21.5, 22.6 (44.1) | 37.3, 43.2 (80.5) | 41.6, 42.6 (84.2) | 105.7, 106.1 (211.8) |
While the All Reduce and Reduce + Broadcast performance are comparable, Reduce Scatter + All Gather take a much longer time as compared to the other two approaches. This is due to the fact that Reduce Scatter + All Gather is unable to take advantage of pipelining when the kernels are launched back to back.
Discussion
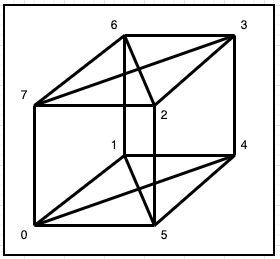
What is the topology of GPUs in Puzzler 1 called?
It is commonly referred to as the Hypercube toplogy. The GPUs can be viewed as vertices of a cube as shown in the figure below.
Hypercube topology
What are the different algorithms and protocols available in NCCL?
The available algorithms in NCCL are:
- Ring
- Tree
- CollNet
In the Ring and Tree algorithms the GPUs form a ring and tree respectively. CollNet is more sophisticated. It can be used only when Infiniband is available. At a high level CollNet creates hierarchical rings and the Ring All Reduce can be broken down as: Inter-node Reduce Scatter followed by Intra-node All Reduce and then an Inter-node All Gather.
The protocols available in NCCL are:
- Simple
- Low Latency (LL)
- Low Latency 128 (LL128)
The protocol can be specified using the NCCL_PROTO environment variable although the environment variable is primarily for debugging purposes only. For more details on the protocols, please see here.
How does NCCL determine which algorithm and protocol to use for any given collective operation?
NCCL implements an Auto Tuner which computes heuristics for all possible algorithm and protocol combinations for all the collectives. The Auto Tuner executes once when NCCL is initialized. It performs an analysis for different combinations of algorithms and protocols and caches the results for subsequent use. The Auto Tuner uses the number of nodes, number of GPUs per node and the message size as parameters.
Does NCCL take the topology and interconnect into account?
Yes, the NCCL Auto Tuner does that implicitly - the underlying toplogy and fabric determine the performance of the communication collectives along with the algorithms and protocols.
What is the difference between NCCL Tree and Ring algorithms?
The Tree algorithm is available only for the All Reduce collective when the number of nodes is greater than 1.
Can you force NCCL to use a particular algorithm?
Users can specify the algorithm using the NCCL_ALGO environment variable.
Can you bypass NCCL, e.g., by using .to(‘cuda:3’) operations? Is there any performance benefit/loss?
Yes, users can bypass NCCL but it strongly advised not to do so. NCCL implements sophisticated
algorithms and protocols along with efficient pipelining techniques and makes use of underlying
topology and fabric which cannot be mimicked with a naive approach such as using .to('cuda:3').
What should you remember in years to come?
Communication plays a critical role in any distributed system. In the context of distributed training on several thousand GPUs communication libraries like NCCL utilize sophisticated algorithms and protocols which are opaque to a casual user. It is best to leave the communication optimizations to NCCL and domain experts.
Explore more
- NCCL Tests a library to benchmark performance and correctness of NCCL operations.
- Blogs on NCCL 1, 2.
- NCCL on the Summit Supercomputer.
- Learn about SHARP.